Skin Diseases on Hands and Forearms: Diagnosis and Treatment
Author: Dr. Luis Sevinsky, Dermatologist
T he hands and forearms are among the parts of the body most exposed to the sun and the environment. This makes them particularly vulnerable to various dermatological conditions which, although often unnoticed, can be important warning signs that something is not right. Have you ever wondered what those spots, cracks, or redness mean? In this article, Dr. Sevinsky explains the most common skin diseases affecting these areas and what treatment options exist.
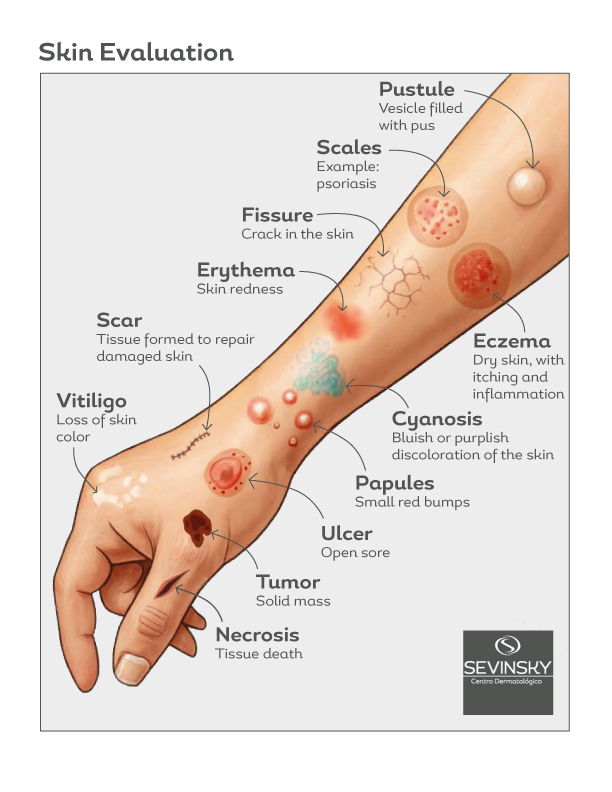
Vitiligo
This autoimmune disease causes the loss of melanocytes, the cells responsible for giving the skin its color. As a result, white patches appear, usually symmetrical and around the mouth, eyelids, and genitals.
Available treatments: topical corticosteroids, immunomodulators such as tacrolimus, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and even melanocyte transplantation or skin grafting.
Solar Lentigines
Also called age spots, these are brown spots of various sizes that appear in sun-exposed areas due to accumulated ultraviolet radiation damage.
Treatments: cryosurgery, laser or intense pulsed light, and most importantly, sun protection with SPF 50 or higher.
Erythema
Redness of the skin caused by increased blood flow, usually due to inflammation, infections, or trauma.
Treatment: topical corticosteroids, antibiotics for bacterial infections, and avoiding contact with irritants or allergens.
Scars
Scars are marks left after a wound heals, due to the formation of new collagen.
Treatment: topical silicone, corticosteroid injections, laser therapy, or plastic surgery.
Fissures
Deep cracks in the skin, often caused by dryness, cold weather, or inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment: intensive moisturizers, topical antibiotics if infection is present, and protective dressings such as patches or bandages.
Scales
Areas of dry, flaky skin, common in conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Treatment: topical corticosteroids, keratolytics such as salicylic acid, and moisturizers.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
A chronic inflammatory disease that causes dry, scaly, and very itchy skin.
Treatment: topical corticosteroids, immunomodulators, moisturizers, and avoiding irritants and allergens.
Dyshidrosis
Appears between the fingers with blisters and intense itching. It is important to rule out fungal infections in other areas, especially the feet. It often affects people with skin allergies.
Treatment: topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines.
Pustules
They are small blisters filled with pus, most often caused by bacterial or fungal infections.
They are treated with topical antibiotics or antifungals, as well as retinoids and benzoyl peroxide.
Cyanosis
Bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes, indicating poor circulation or low oxygen levels.
Management: diagnose the underlying cause (respiratory or cardiovascular problems) and, in some cases, oxygen therapy.
Papules
Small raised bumps on the skin, common in eczema, lichen, or insect bites.
Treatment: topical corticosteroids, antibiotics if infection occurs, and avoiding irritants.
Ulcer
Open wounds on the skin or mucous membranes, caused by injuries, infections, or poor circulation.
Treatment: topical antibiotics, debridement (cleaning), special dressings, and addressing underlying causes such as diabetes or circulatory problems.
Tumor
An abnormal growth of tissue that can be benign or malignant.
Treatment: depends on the nature of the tumor—surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
Actinic Keratoses
Precancerous lesions that appear after years of sun damage, with thickened skin in the affected areas.
Treatment: cryosurgery, 5-fluorouracil, or immunomodulators such as imiquimod.
Necrosis
Refers to dead tissue due to injury, infection, or poor circulation.
Treatment: debridement to remove dead tissue, dressings, and antibiotics.
Purpura
Reddish-purple spots caused by blood leaking outside the blood vessels, due to capillary fragility, sun damage, or trauma.
Treatment: creams with heparinoids and oral arnica supplements.
Concerned About Your Skin Health?
If you have noticed any of these signs or have concerns about your skin health, now is the time to consult an expert. Early diagnosis can make a big difference. Don’t let a simple spot or itch turn into a bigger problem. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Sevinsky for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. Click here to book your visit and take care of your skin health.